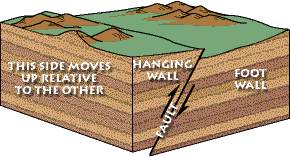
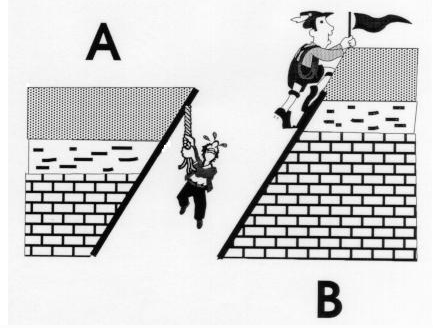
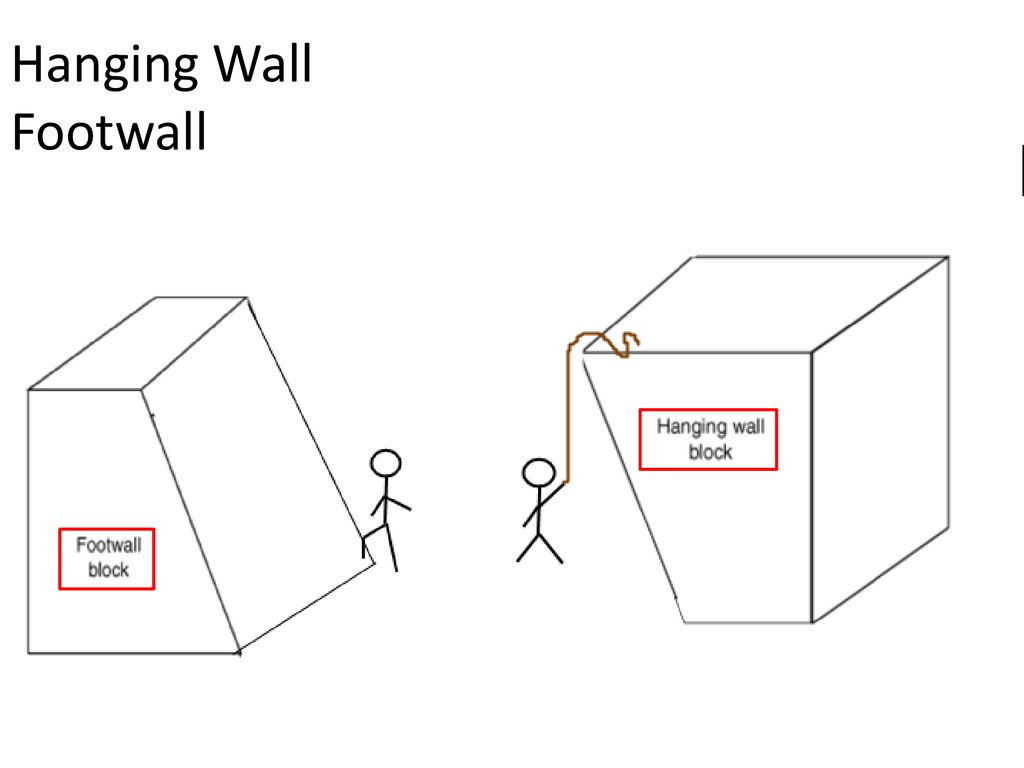
Hanging Wall Rises Relative To The Footwall

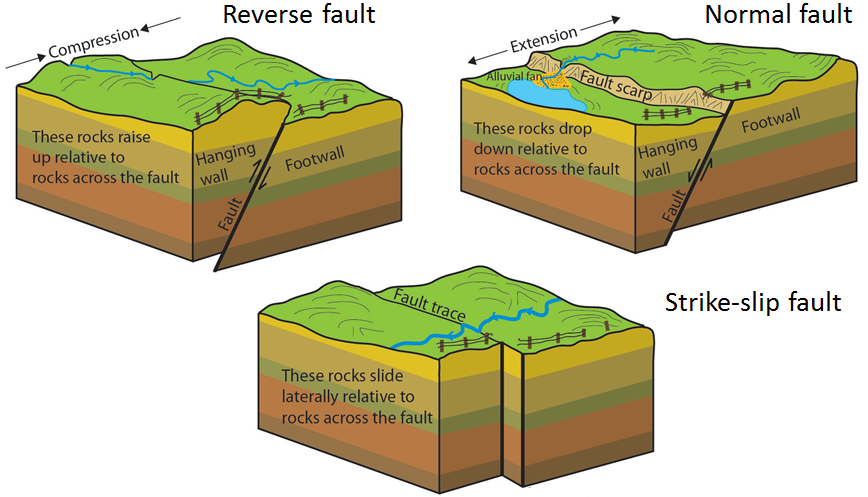
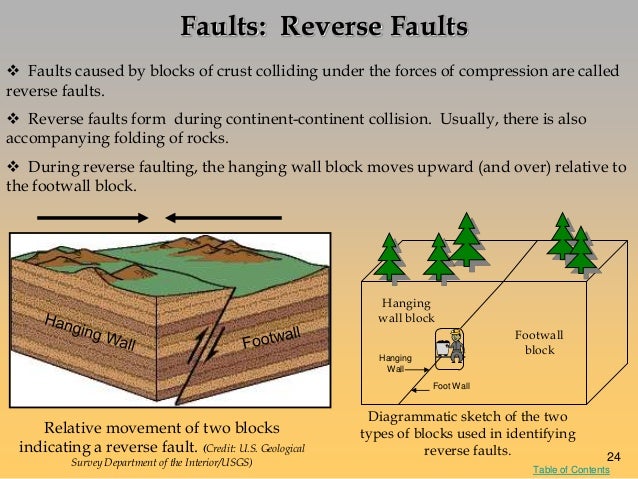
A reverse fault is the opposite of a normal fault the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall.
Hanging wall rises relative to the footwall. The hanging wall rises relative to the footwall. Cliff like landform created by a normal fault. Fault that occurs when two tectonic plates collide. This fault occurs when a hanging wall block has risen relative to its footwall block.
The hanging wall drops relative to the footwall reverse fault fault that occurs when two tectonic plates collide. Horst natural hot water on earth s surface containing many minerals 7. Another type of fault is the thrust fault where ground on one side of the fault moves up and over adjacent ground. If you imagine undoing the motion of a reverse fault you will undo the compression and thus lengthen the horizontal distance between two points on either side of the fault.
Thrust fault a dip slip fault in which the upper. Graben a raised footwall block between normal fault creates. The hanging wall rises relative to the footwall. The hanging wall rises relative to the footwall.
Reverse faults if the hanging wall rises relative to the footwall. Reverse faults occur in areas undergoing compression squishing. Syncline underwater volcano whose top is eroded flat by waves 3. Fault that occurs when two tectonic plates collide.
The hanging wall drops relative to the footwall. Fault that occurs when two tectonic plates are moving apart from each other. If the hanging wall rises relative to the footwall you have a reverse fault. Alternatively such a fault can be called an extensional fault.
Eruption tends to be very explosive. The hanging wall drops relative to the footwall. Volcanic flow that contains a high concentration of gases ash and small rocks. Reverse faults occur in areas undergoing compression squishing.
Hot spring on rolling hills this a dip between hills 4. The hanging wall rises relative to the footwall. Fault that occurs when two tectonic plates collide. A normal fault occurs when the crust is extended.
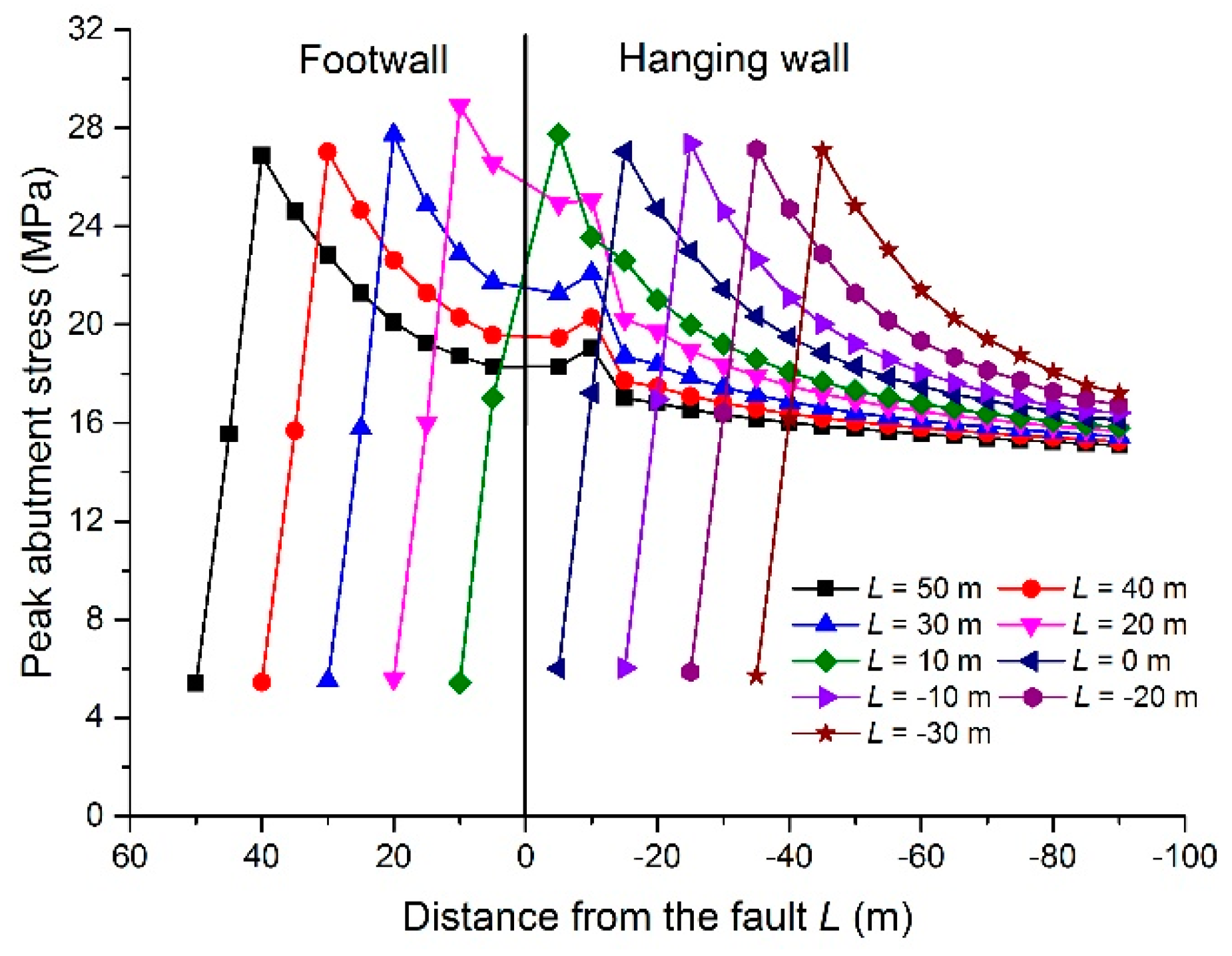
Fault that occurs when two tectonic plates are moving apart from each other. Reverse faults indicate compressive shortening of the crust. Volcanic neck break between rocks where a hanging wall rises relative to a footwall 5. The dip of a reverse fault is relatively steep greater than 45.
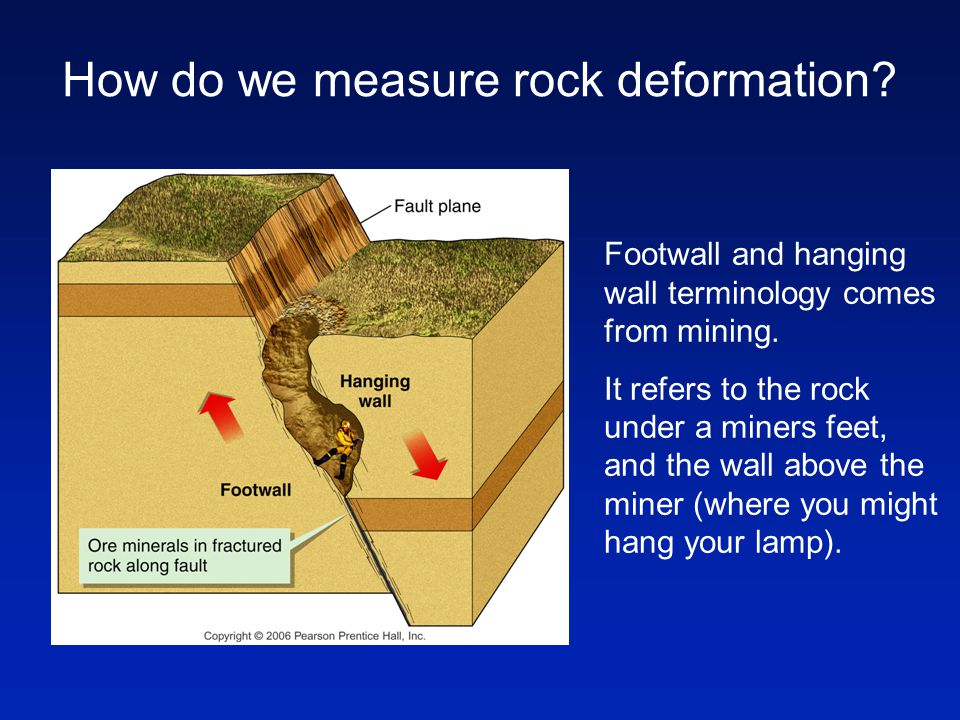
Cliff like landform created by a normal fault. Fault that occurs when two tectonic plates are moving apart from each other. The terminology of normal and reverse comes from coal mining in england where normal faults are the most common. Caldera magma that filled the central vent that remains after the volcano has eroded 6.
Seamount underwater volcano that never reaches above sea level 2.