Heat Sink Fin Orientation

The first plot traveling from the lower left to the upper right is the natural convection curve of heat sink temperature rise tsa versus q.
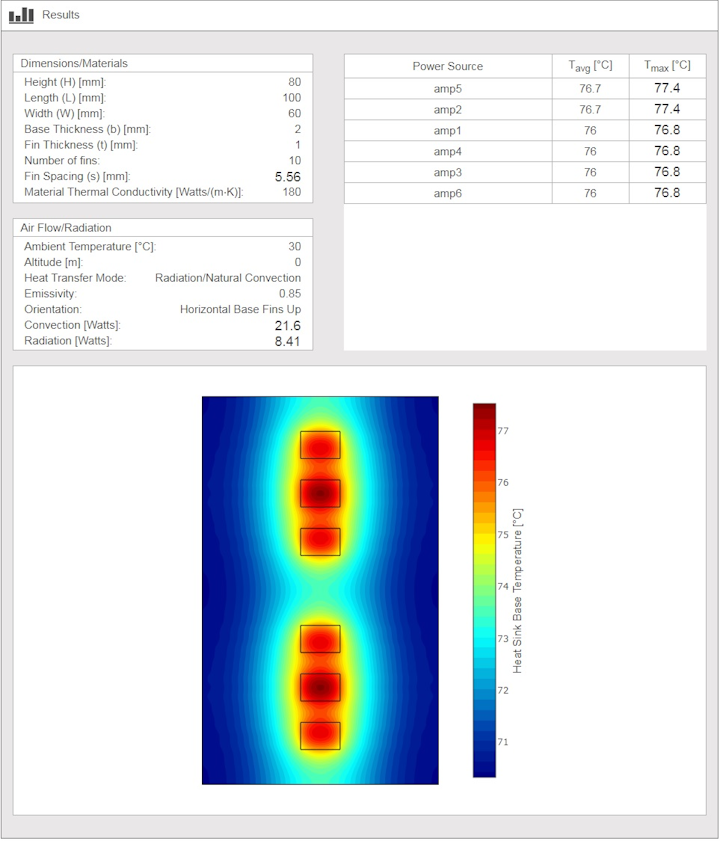
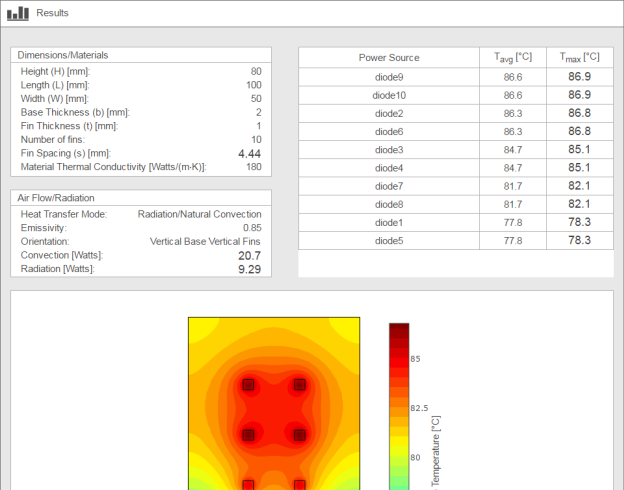
Heat sink fin orientation. However the sideward vertical fin orientation gave the best performance on the natural cooling. And the radiation is omnidirectional. It is assumed that the device to be cooled is properly mounted and the heat sink is in its normally used mounting orientation with respect to the direction of air flow. Typically the fins are oriented in a way to permit a natural convection air draft to flow upward through rectangular u channels or ducts formed by the fins.
Heat sinks are devices that are used to enhance heat dissipation from hot surfaces to cooler ambient air. Air heats and moves up if the fins are horizontal this will be hindered. The effect of orientation of this heat sink relative to gravity field will be offset by the fact that about 1 3 of heat flux will be emitted in the form of radiation if the sink is anodized or painted black which will make the surface emissivity to above 0 9. Test results indicate that the sideward horizontal fin orientation yield the lowest heat transfer coefficient.
Heat sink attachment orientation plays a significant role under natural convection. A trapezoidal fins heat sink with various orientations tested under a controlled environment. It is recommended that the heat sink be installed to orient the fins in a direction that will not block air movement under natural convection. An advantage of bonded fin designs is that the heat sink base and the fins can be of different metals.
The heat sink should be oriented as in fig 1 or fig 2 under natural convection cooling. In which case the orientation of the fins will probably make less of a difference. Wesley lee nov 1 16 at 12 54. The experimental setup is.
Unique fin requirements thermal engineers sometimes need heat sinks with either very tall fins or very thin fins that are tightly spaced. Thermal resistance will probably increase since it will difficult airflow i e. Orientation effects on natural convection heat dissipation of rectangular fin heat sinks mounted on leds 1. Experimental setup and analysis method.